Setting up a help desk system can transform how your business handles support, improves customer interactions, and ensures internal accountability. But success isn't just about the software - it's about proper planning, execution, and continuous improvement. Here's what you need to know:
- Start with Planning: Identify your organization's support challenges, gather input from all stakeholders, and set clear, measurable goals.
- Choose the Right Software: Evaluate platforms for essential features like ticket automation, multi-channel support, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., HIPAA, SOC 2).
- Configure and Test: Define user roles, create efficient workflows, set realistic SLAs, and rigorously test the system before launch.
- Train and Involve Your Team: Provide thorough training, collect feedback, and ensure all stakeholders understand and adopt the new system.
- Focus on Continuous Monitoring: Track key metrics (e.g., response times, CSAT scores), update documentation regularly, and refine processes to meet evolving needs.
A well-executed help desk system leads to faster response times, reduced agent burnout, and improved customer satisfaction. Following these steps ensures a smoother rollout and sets the stage for long-term success.
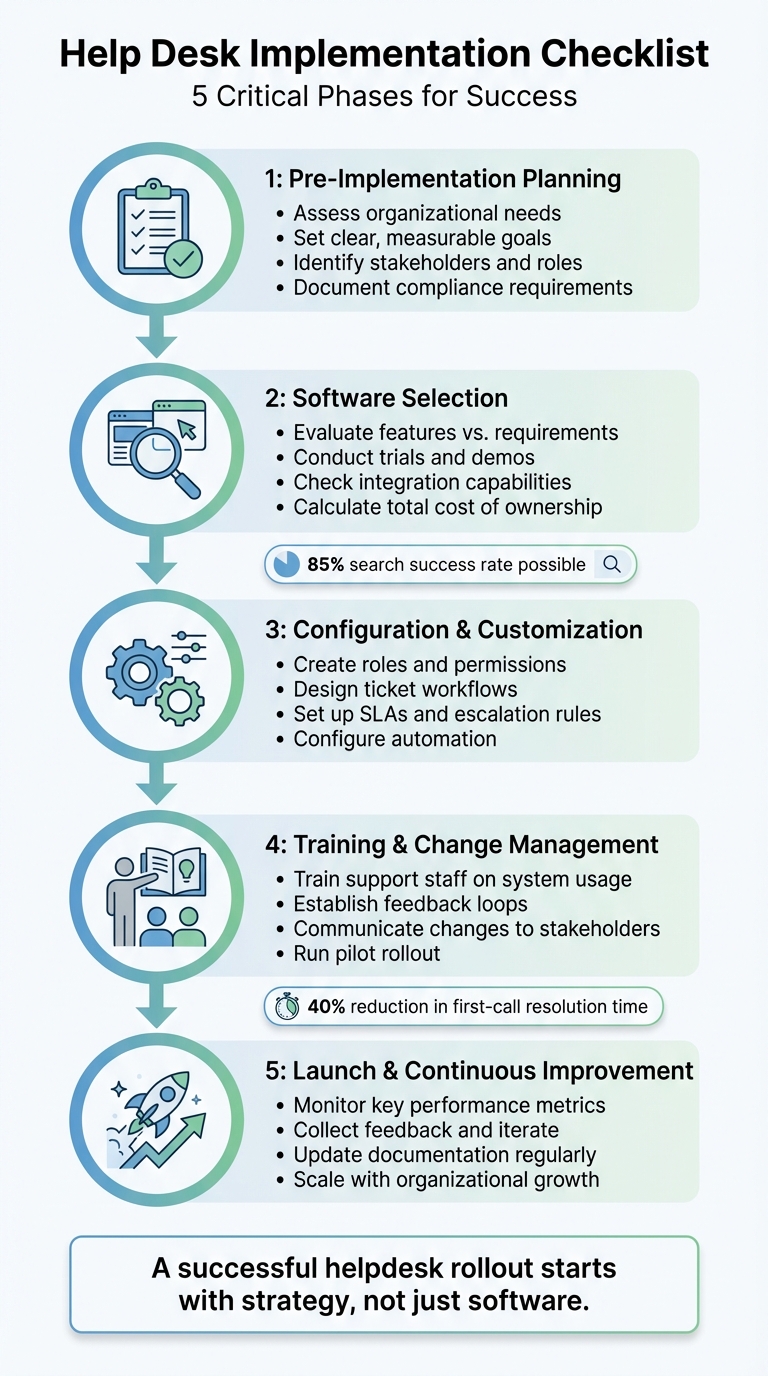
5-Phase Help Desk Implementation Checklist: From Planning to Launch
How to Build a Help Desk (Ticketing) System (+ Free Template)
sbb-itb-e3aed85
Pre-Implementation Planning
Before diving into demos or comparing pricing, it's essential to pinpoint your support challenges. Skipping this step can lead to a help desk system that doesn’t meet your needs - or worse, one that creates more problems than it solves.
"A successful helpdesk rollout starts with strategy, not just software." - Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO of Supportbench
This planning phase might not be the most exciting part, but it’s where success is built. Companies that rush ahead without a solid plan often end up with expensive tools their teams barely use. Taking the time now to evaluate your needs will set the stage for a smoother implementation and better outcomes.
Assess Your Organization's Needs
Start by documenting your current support processes. Map out the journey of a ticket - from the moment a customer contacts you to when their issue is resolved. Look for gaps: Are tickets getting lost in inboxes? Are agents overwhelmed with manual tasks? Is there confusion over who owns which ticket?
Take Wolseley, for example. This major HVAC/R and building materials distributor struggled with their legacy system in July 2025. They lacked visibility into their support operations and frequently missed SLAs. By identifying these issues during their assessment phase, they realized they needed features like automated ticket routing, SLA tracking dashboards, and a self-service portal. Addressing these gaps led to fast improvements in customer satisfaction and gave leadership real-time insights into performance.
Gather feedback from everyone who will use the system - not just management. Support agents, who deal with tickets daily, can highlight time-wasting tasks. IT staff can flag potential security or integration challenges. This collaborative approach ensures you’re solving real problems. According to Gartner, employees who feel engaged and invested in their roles are more likely to improve the customer experience.
Here’s a quick guide to help you assess your needs:
| Assessment Area | Key Questions to Ask |
|---|---|
| Process Gaps | Where are tickets getting delayed or lost? |
| User Roles | Who needs admin access versus standard user permissions? |
| Compliance | Does your data require HIPAA or GDPR-level security? |
| Automation | What repetitive tasks (e.g., password resets) can be automated? |
| Scalability | Will the system handle your team size in 12–24 months? |
If you’re transitioning from spreadsheets or an outdated system, define your data migration needs. Decide which historical data - customer details, ticket history, or knowledge base articles - should be carried over. Also, clarify compliance requirements upfront. For instance, healthcare organizations must meet HIPAA standards and secure a Business Associates Agreement (BAA) from their vendor, while financial firms might require SOC 2 certification. These aren't optional and should be addressed early.
A thorough assessment now simplifies software selection and setup later.
Set Clear Goals and Objectives
Goals like "improve customer service" are too vague to be useful. Instead, set specific, measurable objectives that align with your business priorities. For example, aim to cut first response time from 4 hours to 1 hour, boost first-contact resolution rates by 25%, or reduce ticket volume through better self-service options.
"Setting up a Help Desk is a rare opportunity to change the customer support and service processes and old habits of your support team." - UseResponse
Be realistic about your goals. If your team currently handles 50 tickets per agent daily, don’t set an SLA that requires 100. Overly ambitious targets can lead to burnout and missed deadlines. Instead, categorize requests by urgency and type, then set achievable response times. For example:
- 30-minute response for security incidents
- 1-hour response for critical outages
- 4-hour response for password resets
- 1 business day for new employee onboarding
These tiered goals balance customer expectations with your team’s capacity.
Also, align your help desk goals with your company’s broader plans. If you’re expanding into new markets, you might need features like multi-language support or coverage across time zones. If rapid growth is expected, automation capabilities will be key to managing the increased ticket volume without adding more staff.
Identify Stakeholders and Team Roles
Implementing a help desk system affects multiple parts of your organization, so it’s crucial to involve the right people from the start. Here’s a breakdown of key roles:
- Admins: Handle system configuration, permissions, and global settings. For smaller companies, 5 admins are usually enough to manage the setup.
- Support Agents: They’ll use the system daily, so their input on workflows and usability is vital.
- IT Staff: Manage technical setup, including domain permissions (like SPF/DNS records), security protocols (e.g., MFA or SSO), and tool integrations.
- Supervisors/Managers: Oversee daily operations, monitor performance, and handle escalations.
You’ll also want to include representatives from other departments if the help desk will handle HR, finance, or legal inquiries. These stakeholders can help design workflows tailored to their needs.
| Role | Primary Responsibility in Implementation |
|---|---|
| Admin | Configuring system settings, managing permissions, and overseeing setup |
| Agent | Testing workflows, providing feedback, and managing customer interactions |
| Supervisor | Monitoring team performance, setting escalation procedures, and ensuring SLA compliance |
| IT Specialist | Handling security, integrations, and technical settings |
| Viewer | Accessing reports and analytics without modifying tickets |
Clearly define roles and permissions early to maintain security and accountability. Not everyone needs admin access - limiting it is a good practice as your team grows. Regular communication between admins and agents during the implementation ensures the system is practical, not just theoretical. By assigning clear responsibilities, you’ll create a smoother transition into software selection and configuration.
Selecting the Right Help Desk Software
Once you've documented your needs, the next step is to choose help desk software that aligns with your requirements. This decision is a critical factor in ensuring a smooth implementation process.
"Documenting feature needs and requirements is the most important step in the process of purchasing any new software or cloud service." - Giva
From here, you'll want to evaluate the features of potential platforms to ensure they match your goals.
Evaluate Features Based on Requirements
Start by referring to the list of priorities you created during the planning phase. Pay close attention to core ticketing management features, such as automated ticket routing, categorization, prioritization, and status tracking. The ability to merge related tickets automatically based on agent workload or expertise is also crucial, especially for organizations handling large ticket volumes. Automation is key to avoiding bottlenecks.
Another must-have is multi-channel support. The platform should consolidate requests from email, live chat, phone, social media, and messaging apps. Even today, phone support remains the second most popular communication channel for customers.
Self-service features like a searchable knowledge base or customer portals can significantly cut down ticket volume.
Don't overlook security and compliance. Depending on your industry, you may need specific certifications or agreements. For instance, healthcare organizations often require HIPAA compliance and a Business Associates Agreement (BAA), while financial firms might need SOC 2 certification. Basic security measures like data encryption (both at rest and in transit) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are essential.
When it comes to reporting and analytics, look for tools that provide real-time dashboards tracking key metrics like First Response Time (FRT), Ticket Resolution Time, and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores. These insights can help you identify trends early and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
Here’s a quick look at pricing for some popular platforms:
| Tool | Best For | Starting Price (Billed Annually) |
|---|---|---|
| Freshdesk | Ticket-based workflows | From $19/user/month |
| Zoho Desk | Tailored assistance | From $7/user/month |
| Hiver | AI-powered ticketing/collaboration | From $25/user/month |
| Atera | AI-powered ticket automation | From $149/technician/month |
| SuperOps | Full context tickets | From $89/user/month |
| Missive | Unified inbox collaboration | From $14/user/month |
Keep in mind that base license fees often don't tell the full story. Some vendors may charge extra for API usage, premium integrations, or additional storage. Be sure to factor in costs like implementation, training, and data migration when calculating total cost of ownership (TCO).
Once you've identified a platform that meets your needs, it's time to put it through its paces.
Conduct Trials and Demos
Testing is a non-negotiable step. A trial period allows you to validate how the software fits into your workflow and uncover any usability issues.
"A trial run is your safety net. Before fully committing, simulate real workflows to catch friction points and ensure team readiness." - Eric Klimuk, Founder and CTO, Supportbench
Use sandbox environments to experiment with features without impacting live customer data. Simulate real scenarios - like handling complex technical queries or resolving billing disputes - to gauge the system's performance.
Involve your frontline agents during testing. Their hands-on experience with mock tickets, canned responses, and reporting tools can help refine templates, permissions, and settings before a full rollout.
This is also a good time to assess the vendor's support quality. Submit test tickets and evaluate their response times and helpfulness. If a vendor doesn’t offer a trial or demo, consider it a warning sign.
Check Integration Capabilities
Your help desk software should work seamlessly with your existing tools to prevent data silos and redundant tasks. Start by reviewing your current systems, such as CRM platforms, communication tools, and project management software.
Understand the difference between native integrations - which are quicker to set up - and custom integrations requiring API or webhook development. For example, Jira Service Management offers over 800 marketplace apps to expand functionality without custom builds.
Check for API limits during your evaluation. Some vendors cap the number of API calls or charge extra for high-volume data transfers, which can affect your TCO if you're syncing thousands of records daily.
For identity and access management, ensure the platform supports Single Sign-On (SSO), SAML, and SCIM. These features simplify user management and reduce password fatigue.
Involve your IT team early on. They can address potential compatibility issues, configure SPF and DNS records for secure email delivery, and flag any security concerns.
During trials, test integrations with real data rather than sanitized examples. For instance, create a ticket in your CRM and verify that it syncs correctly with the help desk. Similarly, send a message in Slack and confirm it generates a properly formatted ticket.
Explore SaaS Options in Directories
With so many help desk tools available, narrowing down your options can feel overwhelming. A great resource to explore is the All SaaS Software Directory, curated by John Rush. This directory provides a centralized overview of various platforms, covering categories like communication tools, software development solutions, and business operations platforms.
Using a directory like this allows you to compare platforms side-by-side, review features, and identify those that meet your specific needs. It also simplifies vendor research by letting you access demos, user reviews, and websites in one place.
System Configuration and Customization
Tailor your help desk software to match your team's specific workflows. Start by defining roles, creating ticket workflows, and setting up SLAs to keep operations running smoothly.
Create Roles and Permissions
Use your stakeholder map to establish clear access levels and secure your system. Assign roles like Administrator, who manage system settings, users, and integrations. Keep this group small - ideally no more than five people - to maintain tight control of high-level access.
Supervisors or Managers handle daily operations, monitor team performance, and manage escalations, while Agents focus on resolving tickets and assisting customers. For those who only need to view information, assign Viewer roles with read-only access to tickets and reports.
Instead of assigning permissions individually, organize agents into groups based on expertise, such as Billing, Technical Support, or Sales. This simplifies ticket routing, ensuring requests are sent to the right team right away. For B2B clients, consider adding a Customer Manager role. This allows them to oversee all tickets from their organization without needing to be copied on every request.
To protect sensitive information, implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). For example, HR or legal tickets should only be visible to their respective teams. strengthen security further by enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) or Single Sign-On (SSO) for high-privilege accounts, or by using secure email solutions.
Design Ticket Workflows
With roles in place, focus on creating efficient ticket workflows. A well-designed workflow ensures users see ticket submission as the fastest way to get help. If calling directly is quicker, users may bypass your system altogether.
Standardize ticket categories using a taxonomy that includes Issue Type, Category, and Subcategory. This makes data easier to analyze and avoids creating unstructured noise.
Prioritize tickets based on their impact rather than the order they arrive. Use an impact-based prioritization matrix to calculate urgency. For instance, a system outage affecting hundreds of employees should take precedence over a single user's password reset.
Assign each ticket a single point of contact to ensure consistency, even if the issue is escalated internally. This prevents users from having to repeat their concerns to multiple agents. For complex cases, consider an intelligent swarming model, where specialists collaborate in real time instead of passing tickets through multiple tiers.
Automate routing rules to avoid delays. Use Round Robin for general queues and Skill-Based Routing for specialized requests. Include "Stop the Clock" states - like "Pending User" or "Vendor Wait" - to pause SLAs during periods outside your team's control, ensuring accurate metrics.
To maintain a clean ticket queue, apply a "3-Strike Rule" for unresolved tickets waiting on user input. Send reminders at 24 and 48 hours, and close the ticket automatically after 72 hours with instructions on reopening if needed.
Set Up SLAs and Escalation Rules
After refining workflows, establish SLAs to set clear service expectations. Use recent support data to set achievable targets. Unrealistic goals, such as reducing response times from 6 hours to 1 hour overnight, can lead to team burnout and missed SLAs.
"SLAs are the promises that keep teams aligned, customers happy, and businesses running smoothly. When done right, a help desk SLA does not just set expectations; it builds trust." - Jennifer Akinyi Odhiambo, BoldDesk
Build SLAs around three key metrics: Response Time (how quickly you acknowledge), Resolution Time (how quickly you solve), and Issue Prioritization (how urgency is classified). Limit ticket categories to 5–8 groups, ensuring each reflects genuine differences in urgency or complexity.
| Priority Level | Example Issue | Target Response | Target Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Critical | System Outage / Security Issue | 30–60 Minutes | 4 Hours |
| High | Major Functionality Bug | 1–4 Hours | 1 Business Day |
| Medium | Onboarding / Password Reset | 4–8 Hours | 1–2 Business Days |
| Low | Feature Request / Inquiry | 12–24 Hours | 3+ Business Days |
Set alert thresholds to prevent SLA breaches. For example, send a quiet reminder when 25% of SLA time has passed, escalate to a supervisor at 75%, and take formal action at 90%. This ensures issues are addressed before deadlines are missed.
Pause SLA timers when tickets are marked "Waiting on Customer" or "Waiting on Third Party." Tracking delays outside your team's control can skew metrics and erode trust. Use auto-assignment to avoid idle tickets - every minute counts once the SLA clock starts.
Involve your support team in this process. Frontline agents often have the best insight into bottlenecks and realistic targets. With 75% of customers expecting assistance within 5 minutes, balancing ambitious goals with achievable outcomes is essential for both team morale and customer satisfaction.
Team Training and Change Management
Once you've set up roles and workflows, the next step is making sure your team knows how to use the new system effectively. A help desk only succeeds when the team is well-trained and open to the changes. Training isn’t just a one-and-done event - it’s an ongoing effort that involves structured onboarding, continuous feedback, and clear communication.
Train Support Staff on System Usage
Divide training into three main areas: fundamentals, efficiency, and customer experience. Start with the basics, like understanding the ticket lifecycle, crafting clear responses, and using templates. Then, move on to skills that improve efficiency, such as resolving issues on the first contact, maintaining internal notes, and using troubleshooting documentation. Finally, focus on customer experience by teaching agents how to handle difficult users, provide proactive updates, and track satisfaction metrics.
Key features like the unified inbox, macros, and ticket view management should be part of the training to help prioritize workloads. Familiarize staff with AI tools, such as ticket summarization, draft replies, and sentiment analysis, which can help identify frustrated customers early.
Pair new agents with experienced team members for one or two days to observe how the system is used in real scenarios. Provide quick-reference guides and templates for common situations to maintain consistency in responses. Encourage agents to contribute to the knowledge base directly from the ticket view, which can reduce simple customer queries by 20–35%.
"Training helps new agents get familiar with the company's policies and procedures, as well as the customer service skills needed to provide a successful help desk experience." - LiveAgent
Redirect any off-system requests, like emails or walk-ups, back into the help desk platform to reinforce usage habits. Tie system usage and data accuracy to performance metrics to encourage adoption. Once the team is trained, focus on collecting and using their feedback to refine processes.
Establish Feedback Loops
Start by beta-testing the system with a small group of agents to identify workflow challenges. Use a sandbox environment to let staff practice typical tasks and report usability issues. During the rollout, schedule daily check-ins or pulse surveys to quickly address problems like slow interfaces or missing features.
"Your agents are the first to notice friction - missing features, sluggish response, confusing UI. Make space for daily check-ins or pulse surveys during the rollout week to surface issues early." - Eric Klimuk, Founder and CTO, Supportbench
OpenTable's IT help desk is a great example. In 2023, they surveyed employees and found the ticket submission process cumbersome. By adding more submission channels and automating status updates, they improved perceptions of responsiveness. Follow-up surveys confirmed the changes had a positive impact.
Automate satisfaction surveys to gather feedback when tickets are closed. Ask agents where they encounter roadblocks or if automations are causing confusion instead of saving time. Measure how much effort tasks require to pinpoint workflows that might be too complex.
Create dedicated channels on platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams for agents to share usability issues and suggest improvements. During implementation, give lead agents administrative permissions so they can adjust settings based on team needs. Use input from pilot users to fine-tune permissions, templates, and system settings before a full rollout.
Communicate Changes to Stakeholders
Once internal feedback is addressed, ensure all stakeholders understand and support the new system. Employees are more likely to accept changes when they grasp the reasoning behind them. Research shows that 33% of U.S. employees don’t understand the purpose of organizational changes, which contributes to the failure of 70% of change initiatives. Start by briefing directors and managers so they can guide their teams before making a company-wide announcement.
"People are naturally resistant to change, but clear and specific communication can help your team feel included, aware, and prepared." - Sarah Olson, Senior Associate, Content Marketing, Zendesk
Adapt instructions and resources for different groups. For example, sales reps and support agents will interact with the system differently, so tailor cheat sheets, walkthroughs, and FAQs accordingly. Use multiple channels like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and internal knowledge bases to reinforce the message.
Be transparent about major changes. Face-to-face meetings or video calls show respect and emphasize the importance of these updates. Acknowledge that older shortcuts or "shadow processes" were created for efficiency and demonstrate how the new system is faster to win over skeptics. If stakeholders revert to outdated methods like direct emails, gently redirect them to the new system to establish long-term habits.
Leadership plays a key role in reinforcing change. When leaders actively use the new system and redirect off-platform requests, it sets an example for others. To ensure a smooth transition, run the new help desk alongside the old system briefly during rollout to avoid service disruptions and monitor stability. Use surveys and Q&A sessions to assess awareness and readiness, treating workarounds as useful feedback rather than resistance.
Testing and Quality Assurance
After all the planning and setup, rigorous testing is your safety net against costly errors. It ensures that any potential issues are identified and resolved early, saving time, money, and headaches later. A well-structured testing phase is critical to avoid post-launch failures that could disrupt customer service and harm your operations.
"A thorough QA process is one of the most important Best Practices for a successful migration. It's your final line of defense against the chaos that a botched migration can cause." - ClonePartner
The next step is validating all core functionalities in a controlled environment.
Conduct Functionality Testing
Start by testing every channel and feature in a sandbox or staging environment to avoid affecting live data. For voice systems, check greetings, IVR menus, call routing, and ensure warm and cold transfers function properly. Test voicemail delivery for accuracy and verify that holiday settings work as expected.
For email, confirm that DKIM and SPF records are properly verified. On chat platforms, test widget designs and ensure proactive campaigns trigger as intended. Social media integrations should route messages correctly and allow agents to respond without issues.
Examine the ticket lifecycle across all channels (email, API, social media, etc.). Confirm that ticket details appear correctly and in order, and ensure agents can search for tickets, contacts, and knowledge base articles with ease. Test workflows, automations, and business rules to ensure tickets are routed to the right agents or departments. Verify SLA timers, escalation rules, and overdue alerts are functioning as planned. Ensure seamless data flow with third-party tools like Salesforce, Jira, or Slack, and check that knowledge base articles are well-organized with working links.
Make sure Single Sign-On (SSO) works for all agents and that the system meets hardware and browser requirements. Simulate high ticket volumes, run reports during peak times, and test usability on various mobile devices to confirm smooth performance for agents and customers alike.
Run User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
While functionality testing ensures the system works technically, UAT addresses a different question: "Does this system meet the needs of the people who will use it?" UAT involves real users and subject-matter experts testing the system in real-world scenarios. This phase typically lasts 2 to 10 business days, depending on the system’s complexity.
"UAT answers the question 'Did we build the right thing?' (not just 'Did we build it correctly?')" - UI Zap
For instance, during a 5-day UAT, a healthcare provider uncovered workflow issues that, once resolved, significantly improved user satisfaction and efficiency. On the flip side, an e-commerce platform that skipped UAT faced 47 customer complaints within 24 hours of launch due to VAT calculation errors, leading to costly delays and rollbacks.
Use realistic production data during UAT to catch issues synthetic data might miss - like special characters or unusual formats. Write test scenarios in plain language (e.g., "Process a refund for a VIP customer") so business users can test independently. Assign testers the exact security roles they will use in production, rather than generic admin roles, to validate permissions.
Don’t just test the "happy path" - include edge cases like unauthorized access attempts or system rollbacks. Hold short daily triage meetings to prioritize and address new defects. Define clear exit criteria, such as achieving a 95% scenario pass rate with no critical (P0/P1) defects remaining, before considering UAT complete.
Once UAT confirms the system meets user needs, move on to a controlled pilot rollout to validate adoption in real-world conditions.
Implement a Pilot Rollout
A pilot rollout lets you test the new help desk system with a small group of users or for specific use cases before launching it organization-wide. This approach reduces risks and builds confidence through early successes. Choose a limited audience, such as a single department or product line, and focus on users who are eager to adopt the system and have clear pain points.
"A successful helpdesk rollout starts with strategy, not just software." - Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO, Supportbench
Begin by populating the system with high-value content, like the top 20 FAQs or common internal SOPs, to test its effectiveness without overwhelming users. Before granting access, double-check search relevance, link functionality, and permissions.
During the pilot phase, track key metrics such as search success rates, failed queries, ticket volume, and resolution times. These insights can help you identify content gaps or technical issues. Research shows that well-executed knowledge bases in call centers can achieve search success rates of around 85%, while effective help desk systems can reduce first-call resolution times by about 40%. Use the data to make quick adjustments, like refining article titles, tweaking automation rules, or fixing permission errors.
Run the new system alongside the legacy one for a short overlap to prevent service disruptions. During the initial 24 to 72 hours post-launch, offer "Hypercare" support to quickly address any emerging issues and ensure a smooth transition.
Launch, Monitoring, and Continuous Improvement
Once the pilot phase is complete, it's time to roll out the help desk system across your organization. But the work doesn’t stop there. The real challenge begins post-launch: keeping a close eye on performance, gathering feedback, and tweaking processes to ensure the help desk keeps up with your organization’s changing needs.
Monitor Key Performance Metrics
Start by keeping tabs on metrics in four main areas: Productivity (ticket volume, backlogs, agent utilization), Customer Impact (CSAT scores, Net Promoter Score, SLA compliance), Agent Performance (first response time, first contact resolution, average handle time), and Financial Impact (cost per ticket, ROI). A real-time dashboard can help you track trends and compare performance over time. Ideally, tickets opened and tickets solved should follow similar patterns.
Set up automated checks every 10 minutes to catch SLA breaches and send out email alerts. Clearly display SLA targets on dashboards and alerts to keep response goals front and center. For metrics like CSAT, calculate it by dividing satisfied responses by total survey responses and multiplying by 100. First Contact Resolution (FCR) can be tracked by dividing tickets resolved on the first try by total tickets handled, then multiplying by 100.
Use benchmarks informed by industry standards, past performance, or internal trends to measure progress. To ensure accurate reporting, log all requests in the system - no exceptions.
These metrics provide a solid foundation for identifying areas that need improvement.
Collect Feedback and Iterate
While metrics tell part of the story, qualitative feedback reveals what numbers can’t. Automate CSAT surveys to send immediately after ticket closure to assess user satisfaction. Schedule regular meetings with IT teams, management, and end users to discuss system performance and gather suggestions.
"The path to successful SaaS implementation isn't all smooth. The resistance to change among team members poses a significant challenge. The best way to overcome this is to implement comprehensive training programs and conduct regular sessions to educate the team on the benefits of the new system." - Fawaz Naser, CEO, Softlist.io
Talk directly with support agents to uncover workflow bottlenecks, and gather customer anecdotes to surface problems that data alone might miss. Use the HEART framework (Happiness, Engagement, Adoption, Retention, and Task Success) to measure how users interact with the system. Start with straightforward automations like ticket categorization and instant acknowledgments before tackling more complex workflows. Personalize canned responses to keep the tone human and engaging, avoiding robotic-sounding replies.
As your organization grows, adapt your help desk structure to scale with it. Analyze ticket distribution to spot recurring issues and expand your knowledge base to empower self-service.
The insights gathered here will guide the next critical step: keeping documentation current.
Update Documentation Regularly
Keeping your documentation up-to-date is essential for effective training and ongoing improvement. Maintain a robust knowledge base with updated guides, walkthroughs, and solutions to frequent issues. Create a master playbook to capture institutional knowledge and use it as a training resource. Regularly refresh troubleshooting scripts and checklists based on team feedback and changes in your technical environment.
Streamline initial ticket submission forms by asking only for key details like category, urgency, and a brief description. This reduces barriers for users. Introduce condition-based actions in forms to ensure consistent data collection while keeping the process simple. For technicians, maintain a more detailed service catalog with approval workflows, security details, and technical manuals to enable efficient service delivery.
Identify services that are frequently requested - like password resets - and move them to self-service options. This shift-left approach can free up IT resources for more complex tasks. Lastly, double-check that role-based access controls are properly configured, especially for sensitive areas like HR or Legal.
Conclusion
Creating and maintaining a help desk is an ongoing effort that reflects your organization's commitment to meeting evolving needs. The key to success lies in prioritizing strategy over software. Before diving into platform evaluations, it's crucial to set clear objectives - whether that's cutting down backlog or achieving a common goal like resolving 95% of queries within 24 hours.
The checklist you’ve followed - from planning to post-launch monitoring - serves as a practical roadmap. It not only ensures a smooth rollout but also lays the groundwork for continuous improvement. As Nooshin Alibhai, Founder and CEO of Supportbench, puts it:
"A helpdesk isn't just where tickets get processed. It's the front line of employee satisfaction, customer service, and internal accountability".
A help desk isn't static - it needs to grow with your team, adapt to new technologies, and meet shifting customer expectations. Start with the basics, focus on measurable goals, and refine your system over time.
The difference between a functional help desk and a high-performing one lies in ongoing improvement. Monitor key metrics like first-response time and CSAT scores, but don’t stop there. Collect qualitative feedback from agents and users to identify issues that numbers alone may miss. Keep your knowledge base current, encourage users to stick with the system for support, and gradually introduce automation - starting with simple tasks like ticket routing before tackling more advanced workflows.
The rewards of a dynamic help desk are evident. Take Wolseley’s July 2025 transformation with Supportbench, for example. By implementing automated routing, SLA dashboards, and self-service portals, they boosted customer satisfaction and reduced agent burnout. This underscores the value of a thoughtful, adaptable help desk strategy.
FAQs
What should I define before choosing a help desk tool?
Before choosing a help desk tool, it's important to pinpoint what your organization genuinely needs. Think about the features you can't do without, how your support workflows function, and what you aim to achieve with the tool. On top of that, take a close look at factors like security, scalability, and integration capabilities. These will help ensure the tool fits seamlessly into your current operations while also supporting your growth down the line.
How do I set SLAs that won’t burn out my team?
To craft SLAs that help prevent team burnout, focus on setting achievable response and resolution goals grounded in data. Organize tasks by their level of urgency, and consider automating repetitive workflows to save time and energy. Keep an eye on team workloads consistently, and tweak SLAs when necessary to ensure a healthy balance and avoid overburdening your team.
What should I test before launching the new help desk?
Before rolling out your help desk, it's crucial to test everything thoroughly to avoid hiccups later. Check how well your system integrations work, ensure automations and workflows run as intended, and verify that ticket handling is smooth and efficient. Pay close attention to the accuracy of data migration, the ease of use of your self-service portal, and how the system performs under typical workload conditions. After migration, conduct quality assurance (QA) to confirm that your data is intact, the system is dependable, and the platform is easy for users to navigate - all before making it live.
